A peptide library contains a great number of peptides that have a systematic combination of amino acids. By producing large numbers of peptides, for which each differs from the other by one single amino acid, it is possible to ascertain which amino acid substitutions make binding to a receptor the strongest, and which make that binding process weaker. The challenge is how to conveniently and cost-effectively create thousands, or even millions of peptides so that they can be utilized in binding studies.
Tanda can synthesize peptide libraries for drug discovery, high-throughput screening, including alanine scans and truncation sets. Tanda utilizes optimized protocols and chemistries to ensure consistent purity, quantity, and quality library-to-library and within each peptide library. And can incorporate most standard peptide modifications within custom peptide libraries. Standard modifications that can be incorporated are unusual amino acids, D-amino acids, C-terminal amidation, N-terminal modification, and biotin, dye or fluorescence labeling on the N-terminal or lysine side chains.
Tanda can offer a wide range of library design options to increase the potency of a lead peptide. Each can be tailored to address specific research questions.
A. Libraries of overlapping peptide sequences
They are usually designed from a larger protein to quickly identify a protein region contributing to a specific functionality. By individually testing the peptides, the protein sequence is screened for the presence of key epitopes.
A well-known application is epitope mapping
Overlapping peptide libraries can also be screened for identifying the peptidic region within an antigenic protein which is responsible for a T-cell response.

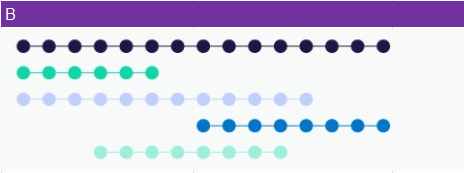
B. Libraries of unrelated peptides
Peptides of different lengths, are a cost-effective solution for simultaneously screening a large set of peptides in a defined application.
C. Alanine scanning libraries
Each amino acid position of the peptide is sequentially replaced with an alanine.
Alanine, the smallest chiral amino acid, is used to substitute each non-alanine residue within the sequence while not drastically affecting the conformation of that protein region.
This allows identifying the specific amino acid residues contributing to a peptide function, e.g. a protein-protein interaction or ligand-receptor binding activity.

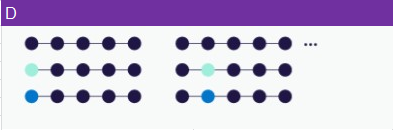
D. Positional scanning libraries
These are designed by substituting -individually and sequentially- each amino acid with a selection of two other amino acids. This method is frequently used for sequence optimization. The resulting crude mixture is composed mainly of the two corresponding peptides, not necessarily in equimolar amount.
Tanda offer high-throughput screening (HTS), affinity-based screening (SPR, BLI, ELISA), and functional screening (cell-based and enzymatic assays). These technologies allow us to identify peptides with high affinity, specificity, and desired biological activity.
Comprehensive expertise
Our team comprises experts in peptide chemistry, molecular biology, bioinformatics, and pharmacology, ensuring a multidisciplinary approach to peptide library construction and screening.
Cutting-edge technology
We utilize the latest technologies and methodologies, including automated peptide synthesizers, high-throughput screening platforms, and advanced computational tools, to deliver high-quality results.
Customization and flexibility
We offer customizable services tailored to the specific needs of our clients, from small-scale pilot studies to large-scale screening projects, ensuring flexibility and scalability.
Speed and efficiency
Our streamlined processes and integrated workflows enable rapid turnaround times, allowing you to accelerate your drug discovery projects and bring novel therapeutics to market faster.
Quality and reliability
We adhere to stringent quality control measures and industry standards, ensuring the reliability and reproducibility of our results.
